Critical thinking is a fundamental cognitive ability that allows individuals to analyze information, identify biases, and evaluate evidence. It is a complex process that involves various cognitive and neural processes.
But have you ever wondered: “What part of the brain controls critical thinking?” This question has puzzled scientists and researchers for decades.
The prefrontal cortex is the part of the brain responsible for critical thinking. It is responsible for controlling complex cognitive behavior, decision-making, and social behavior.
In this blog, we will explore the neuroscience of critical thinking and delve into the functions of specific brain regions that contribute to this essential cognitive skill.
Contents
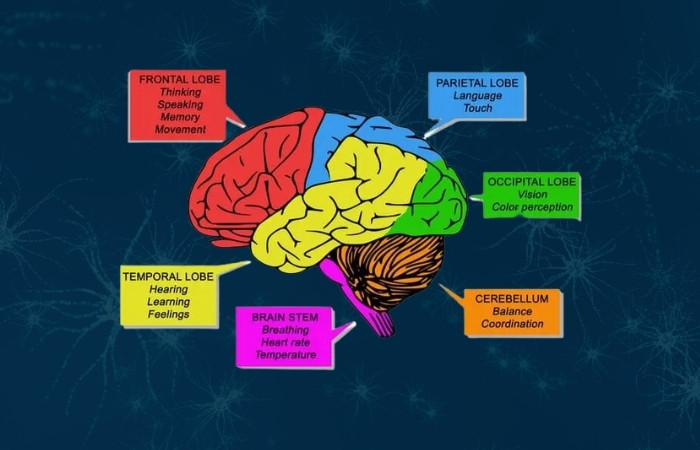
Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works
The human brain is the center of the nervous system, responsible for a wide range of functions including thinking, behavior, movement, and regulating the body. It is made up of several regions, including the brain stem, cerebral cortex, and lobes, such as the frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal lobes.
The cerebral cortex is responsible for higher brain functions, such as language, motor skills, and perception, while the brain stem controls basic bodily functions such as heart rate and breathing.
Typically, left hemisphere of the cortex is typically responsible for language and analytical skills, while the right hemisphere is involved in creativity and spatial perception. The prefrontal cortex is responsible for decision-making and impulse control, while the motor cortex controls voluntary movement and the visual cortex processes visual information.
Relation Between Brain and Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a complex cognitive process that involves analyzing and evaluating information to make sound decisions and solve problems. It is closely linked to the human brain and its various functions.
The prefrontal cortex, located in the frontal lobe of the brain, plays a crucial role in critical thinking, as it is responsible for executive functions such as decision-making, problem-solving, and planning.
Other brain regions such as the parietal lobe, temporal lobes, and occipital lobe are also involved in different aspects of critical thinking such as perception, attention, and memory.
What Part Of The Brain Controls Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking involves a complex network of brain regions and functions. But the prefrontal cortex, located in the frontal lobe of the brain, is believed to play a crucial role.
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for higher-order cognitive functions such as decision-making, planning, problem-solving, and working memory. It is also involved in regulating attention, impulse control, and social behavior.
Damage to the prefrontal cortex can result in impairments in critical thinking and other executive functions. Other brain regions and functions involved in critical thinking include the parietal cortex, the temporal lobes, and the left hemisphere.
How Critical Thinking Develops In The Brain?
Critical thinking involves various cognitive processes, including perception, attention, memory, and reasoning. These processes develop and interact in different regions of the brain, such as the prefrontal cortex and parietal lobes.
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for planning, decision-making, and problem-solving, while the parietal lobes process sensory information and support spatial awareness.
Through experience and practice, these brain regions form connections and networks, leading to improved critical thinking skills. Additionally, exposure to diverse perspectives and challenging information can promote the development of critical thinking abilities.
5 Factors Affecting Critical Thinking
Several factors can affect an individual’s ability to think critically. In this response, we will discuss five factors that can affect critical thinking, namely age, gender, environmental factors, genetics, and diseases.
Age
Age is a significant factor that can affect critical thinking. Research has shown that critical thinking skills develop with age and experience. As individuals age, they tend to gain more knowledge, expertise, and life experience, which can enhance their critical thinking abilities. However, as individuals get older, they may also experience cognitive decline, which can impact their critical thinking skills.
Gender
Gender is another factor that can affect critical thinking. While there is no evidence to suggest that one gender is more capable of critical thinking than the other, studies have shown that males and females may approach critical thinking tasks differently.
For example, some studies have suggested that males may be more inclined towards analytical thinking, while females may be more inclined towards critical thinking.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors can also play a significant role in critical thinking. The environment in which an individual grows up, works, or lives can affect their critical thinking skills.
For example, individuals who grow up in environments that encourage open-mindedness and curiosity are more likely to develop strong critical thinking skills.
On the other hand, individuals who grow up in environments that discourage questioning and independent thinking may struggle with critical thinking.
Genetics
Genetics can also play a role in critical thinking. While there is no specific “critical thinking gene,” research has suggested that certain genes can impact cognitive function and, in turn, critical thinking skills.
For example, studies have shown that individuals with a genetic variation that affects the prefrontal cortex may have lower critical thinking abilities.
Diseases
Certain diseases can also affect critical thinking. For example, dementia and Alzheimer’s disease can cause cognitive decline and impair critical thinking skills.
Additionally, conditions that affect specific areas of the brain, such as strokes or traumatic brain injuries, can impact critical thinking abilities by damaging specific brain regions that are involved in critical thinking.
Read to Know: What Is Argument In Critical Thinking
How to Improve Critical Thinking Skills? 7 Ways
Critical thinking involves using our cognitive abilities to question assumptions, evaluate evidence, and consider different perspectives. Here are some ways to improve your critical thinking skills.
1. Develop Your Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the part of the brain responsible for decision-making, problem-solving, and critical thinking. To improve these skills, you can engage in activities that stimulate the frontal lobe, such as puzzles, brain teasers, and strategy games.
2. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise has been shown to improve cognitive function, including critical thinking. Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, which helps to nourish brain cells and improve brain function.
3. Read and Learn
Reading and learning about different subjects can help you develop critical thinking skills. It exposes you to new ideas and perspectives, which allows you to evaluate information from multiple sources.
4. Practice Questioning
To improve critical thinking, you need to practice questioning assumptions and beliefs. When you encounter information, ask yourself: Who is the source of this information? What is their agenda? What evidence supports their claims?
5. Engage in Debates
Engaging in debates with others allows you to practice critical thinking skills by evaluating different viewpoints and evidence. It also helps to develop your communication skills and ability to articulate your thoughts and ideas.
6. Develop Analytical Skills
Analytical skills are essential for critical thinking. You can develop these skills by breaking down complex problems into smaller components, identifying patterns and relationships, and using logical reasoning to solve problems.
7. Practice Self-reflection
Self-reflection allows you to evaluate your own beliefs and assumptions. It involves being honest with yourself about your biases and limitations and being open to new perspectives and ideas.
Wrapping Up
We’ve tried our best to clear out “What part of the brain controls critical thinking?” through this content. Typically, critical thinking is a complex cognitive process that is largely enabled by the prefrontal cortex, a part of the brain located just behind the forehead.
This region is responsible for the executive functions of the brain and is associated with higher-order thinking, planning, and decision-making. Various other parts of the brain, including the parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and hippocampus, also play a role in critical thinking, albeit in varying degrees.
Read More:
How Are Symbols Related To Critical Thinking?
What Is The First Step In The Critical Thinking Process?
How Do Emotions Positively And Negatively Influence Critical Thinking?